I finally received one. It was clear as day.
A student in my Propaganda course at Queens College who had barely been able to construct a sentence all semester turned in a final paper with perfect organization and zero punctuation errors. It was as if someone else had written the paper.
That someone was AI.
In previous semesters, I had occasionally encountered papers downloaded from web-based services or simply cut and paste from essays, articles, or even Wikipedia. They were easiest enough to find with a simple web search. As if wanting to be caught, some students have even turned in papers written by other students for previous semesters of my course.
Because I teach at a public college, most of my students are not wealthy to hire tutors or the online academic version of task rabbits to write their papers for them. (A friend of mine who teaches at an elite high school once challenged a student to answer a few basic questions about such a paper to see if he even understood what was on the page. The student’s parents complained, and the teacher was put on suspension for traumatizing the boy.)
ChatGPT levels the playing field, giving students without the money to pay for bespoke papers from anonymous graduate student gig workers an opportunity to produce and submit essays they haven’t written. So far, the results are not at what we would normally consider college level. Yes, the sentences are clear and the organization of the papers is good. Many of my college students have not had the opportunity to learn the basics of nouns, verbs, sentences, and paragraphs, so these papers do stand out. Compared with many of the papers I receive, which have been produced through speech-to-text with no proof-reading, the AI-produced essays are of professional caliber.
So far, at least to an experienced essay reader, they all exhibit telltale signs of synthetic production. The depth of analysis remains exactly constant. There are no aha moments, no incomplete thoughts, no wrestling with ambiguity. It all reads like a Wikipedia article (no doubt where much of the “thinking” has been derived, at least indirectly.)
Still, without proof, it’s hard to accuse a student of writing a paper that looks and feels like it has been generated by AI. And the AI’s will no doubt get better with time. So what’s a teacher to do? Assuming we care, that grades matter, and that as accrediting institutions we need to enforce basic academic integrity, there are a few good alternatives.
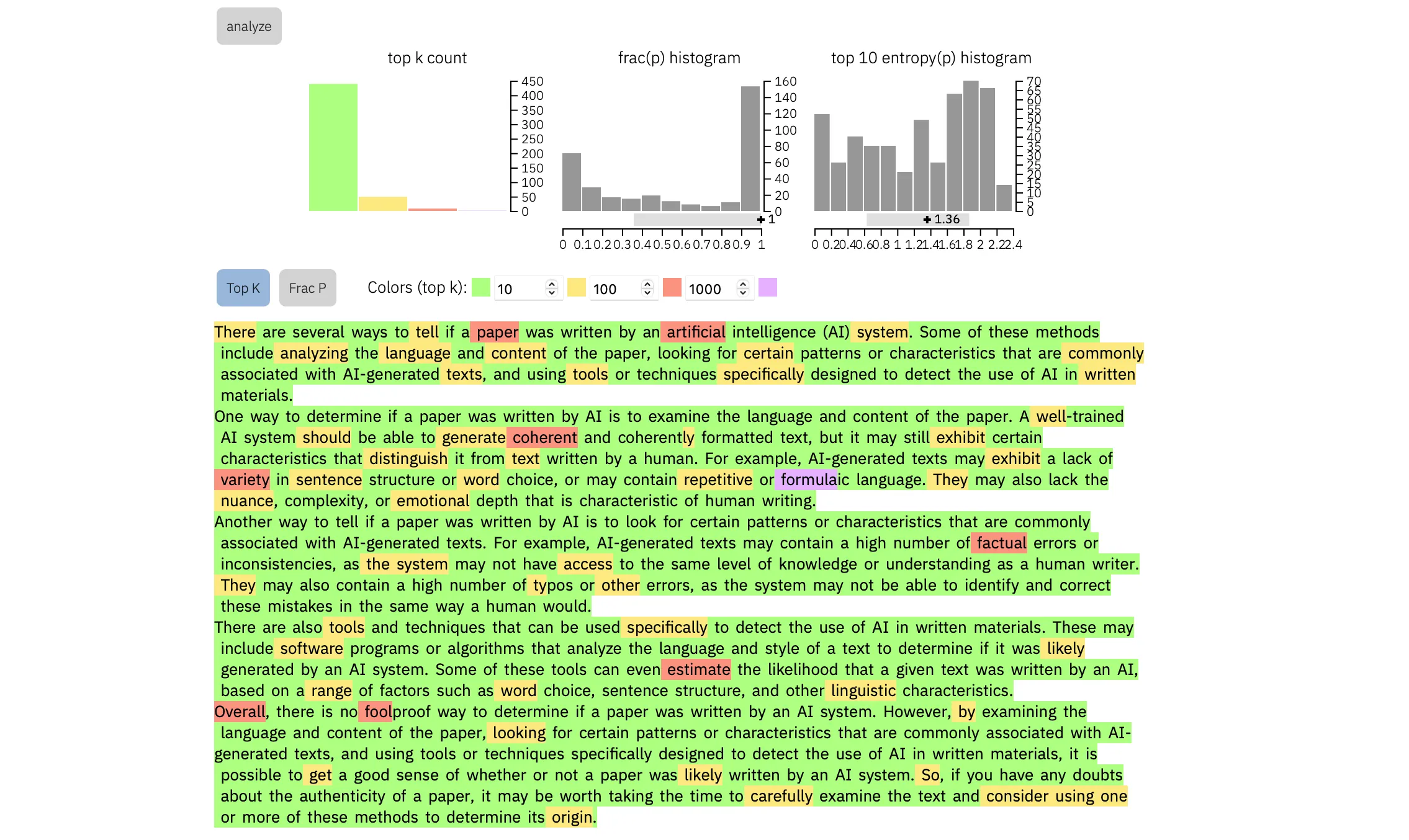
First, and easiest, are free online analytical tools like GLTR, where you can paste the text and determine how predictable each word of the essay is based on the ones it followed. The more predictable the words, the more likely they were produced by an AI. GLTR highlights predictable words in green, and more surprising terms (human ones — what tech people would call “noise” but I would call “signal”) in yellow or red. The essay in the photo above was clearly produced by an AI.
But I’m thinking the problem of students submitting fraudulently produced papers points to a more fundamental issue with how we do education. Instead of entering a technological arms race against cheating students, we need to shift our approach to achievement and assessment. Many professors I know who were educated in Europe had never encountered a “Scantron” answer sheet before coming to the United States. For them, the essay submitted by a student is not the culmination of a semester’s work, but the starting place for a conversation.
Our model of education, with students taking tests and writing essays to “prove” their competency in order to get a passing grade and “credit” toward a degree, is itself a one-size-fits-all artifact of the Industrial Age. I understand why we might want to give competency exams to paramedics and cab drivers before entrusting them with our lives, but a liberal arts education is not a license to practice; it is an invitation to engage with ideas, culture, and society.
That’s a hard culture to engender with 50 or more students in a “seminar”, or several hundred in a lecture, particularly when many colleges can no longer afford Teaching Assistants or graduate students to help read papers. It’s even harder when students are showing up more for the credit than the learning. But the only truly workable response to a student population that has turned to AI to produce its papers is to retrieve the time-consuming, face-to-face interaction that (for me, anyway) constituted the most memorable moments of my education.
Yes, I’m talking about live conversations with students about their ideas, their perspectives on what they have read, or even their responses to my questions about their work. In some sense, we can see the way students have resorted to AI-produced essays as an entirely utilitarian response to an educational culture that has become far too utilitarian, itself. If we want our students to bring their human selves to the table, we have to create an educational environment that engenders human engagement.